开发一个简单的mybatis案例
开发流程:
编写实体po类
编写dao文件接口,写好接口方法,传参使用@param,接口配置为@mapper
编写xml文件
mapper标签:配置好映射的类
sql id=all_column:写好全表结构或常用表结构resultMap id type:写好表字段映射写好实际方法
xml编写
有三种配置方案:
MapperFactoryBean:适合单独Mapper的配置
MapperScannerConfigurer:适合扫包多mapper配置,每个mapper生成bean的时候也是借助MapperFactoryBean完成的
SqlSessionDaoSupport:不咋好用,还得自己重写获取mapper的方法,不如直接用前两个,MapperFactoryBean就是SqlSessionDaoSupport的实现
代码原理可以参考:
配置案例:
// datasourcebean
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/lexueba?useUnicode=true&
characterEncoding=UTF8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="haojia0421xixi"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="100"></property>
<property name="maxIdle" value="30"></property>
<property name="maxWait" value="500"></property>
<property name="defaultAutoCommit" value="true"></property>
</bean>
// SqlSessionFactory的bean
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.Spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:test/mybatis/MyBatis-Configuration. xml"></property>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
// 方案一、MapperFactoryBean配置
<bean id="userMapper" class="org.mybatis.Spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="test.mybatis.dao.UserMapper"></property>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
// 方案二、MapperScannerConfigurer
<bean class="org.mybatis.Spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="test.mybatis.dao" />
</bean>开发PO层、DAO层、SQL映射
PO层、DAO层定义
例如UserPo;定义Dao层,例如UserMapperDAO,提供数据交互接口,将Dao层纳入spring管理
public interface UserMapperDAO {
public void insertUser(User user);
public User getUser(Integer id);
}通过spring管理DAO文件时把映射写入mybatis-config.xml中,可以用mapper单个映射,也可以扫包,即上面xml中的两种配置方法
除此之外,还有一种不使用xml的,即在DAO接口上面加@Mapper注解
mapper开发-SQL映射
总体流程如下:
定义与DAO层接口同名的Mapper文件
设置mapper文件的namespace属性为dao层接口全限定名
在mapper文件中定义方法,方法名就是dao层接口文件中sql语句的id,并保持参数类型和返回值类型一致
注意:
一般maven架构下要求java包和resource包分开,因此要在resource下面创建和Mapper接口一样的目录,例如UserMapperDAO在com.heima.mapper,在resource下面创建就是com/heima/mapper,不能用“.”,因此resource在编译时会将“.”视为文件名
namespace处写全引用名,例如com.heima.mapper.xxxx
XML中的sql id即DAO接口中定义的方法名称
例如:
<mapper namespace=”test.dataDao”>
<select id=”queryAll” resultMap=” java.lang.Integer”>
xxx
</select>
</mapper>使用mybatisX插件可以协助mapper和DAO开发
编写测试类
public class UserServiceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("test/mybatis/applicationContext.xml");
UserMapper userDao =(UserMapper)context.getBean("userMapper");
System.out.println(userDao.getUser("1"));
}详解mybatis-config.xml
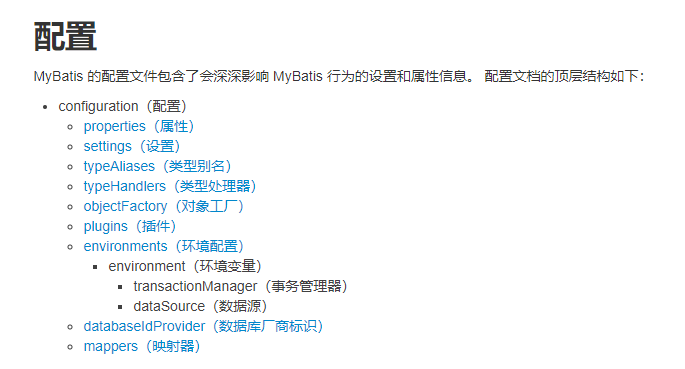
environment是数据库连接信息,可以通过id切换多个数据源
datasource是数据库连接池
typeAliases别名,可以通过typeAliases中间有一个<package>的情况来设定扫包,被扫的包里面的类默认用类名当别名,就不需要在mapper里面写很长的包名了,也可以添加属性alias
配置项举例
1、MapperScannerConfigurer接口方法级扫包配置方法,为了找到与dao文件对应的xml,注册为bean
- <bean id="targetScannerConfigurer" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
|---- property (1) 接口方法扫包路径
|----|--- name=”basePackage”
|----|--- value=”配置mapper接口文件扫包路径”
|---- property (2) sql数据源连接实体
|----|--- name=” sqlSessionFactoryBeanName”
|----|--- value=” SqlSessionFactoryBean的类名”
2、SqlSessionFactoryBean数据源连接,配置mapper位置,为了将sql映射文件xml解析出来
- <bean id="targetSqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
|---- property (1) 数据源
|----|--- name=”dataSource”
|----|--- ref=”数据源类”
|---- property (2) sqlMapper.xml的配置
|----|--- name=” mapperLocations”
|----|--- array
|----|---|--- value=”mapper.xml的路径”
|---- property (3) configuration配置项
|----|--- <bean class="org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration">
|----|---|--- property1
|----|---|--- property2
3、DataSourceTransactionManager数据源事务管理器方法
- <bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
|---- property (1) 数据源
|----|--- name=”dataSource”
|----|--- ref=”数据源类”
3、TransactionTemplate数据源事务模板
- <bean id="transactionTemplate"
class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
|---- property (1) 数据源事务管理器配置项
|----|--- name=” transactionManager”
|----|--- ref=” transactionManager”需注意:MapperScannerConfigurer扫的是dao文件的路径,扫不到xml,真正扫xml是在SqlSessionFactoryBean的参数2中。这个参数可以用mapperLocations,value直接给列表,也可以用configLocation,value给一个实际的xml配置类,再从其中解析。
可以参考如下源码解析:
mapper标签
优雅的结果集 - resultMap
resultMap的作用是在查询时将数据库字段与dto进行一一对应。resultMap的组成元素:
resultMap:一级标签
id:结果集唯一id,也能标志一个结果映射
type:resultMap映射到的java dto类型
constructor:二级标签,实例化类时,注入结果到构造方法中
idArg - ID 参数; 将结果集标记为ID,以方便全局调用
arg -注入构造器的结果集
id:二级标签,标志数据表主键映射到dto的字段
column属性:代表数据表列
property:代表dto字段
result:二级标签,标志数据表其他字段映射到dto的字段
column、property同id
association – 一个关联;一对一的关系,即将结果包装成这种类型
嵌套结果映射 – associations能引用自身,或者从其它地方引用
collection – 一个复杂类型的集合,一对多的关系
嵌套结果映射 – collections能引用自身,或者从其它地方引用
discriminator – 使用结果值来决定使用哪个 resultMap
case – 基于某些值的结果映射
嵌套结果映射 – case 也是一个结果映射,因此具有相同的结构和元素;或者引用其它的结果映射
案例如下:
<resultMap id="blogResult" type="Blog">
<id column="id" property="id"/><!--主键映射-->
<result column="pwd" property="password"/><!--数据库表字段到实体类属性的映射-->
<result column="name" property="name"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectBlogById" parameterType="int" resultMap="blogResult">
select * from blog where id=#{id}
</select>优雅的循环 - foreach
foreach 元素的属性主要有 item,index,open,separator,close,collection。各属性含义如下所示。
item:集合中元素迭代时的别名,该参数为必选。
index:在 list 和数组中,index 是元素的序号;在 map 中,index 是元素的 key。该参数可选。若有,可以把index作为结果插入数据库
open:foreach 代码的开始符号,一般是
open="(",和close=")"合用。常用在in(),values()时。该参数可选。一般用于select in语句separator:元素之间的分隔符,例如在 in() 的时候,
separator=","会自动在元素中间用 “,“ 隔开,避免手动输入逗号导致 SQL 错误,如 in(1, 2,) 这样。该参数可选。close:foreach 代码的关闭符号,一般是 ”)“,和
open="("合用。常用在in(),values()时。该参数可选。collection:要被 foreach 标签循环解析的对象。foreach 标签的 collection 属性在接受参数名时,有两种情况:
匿名参数:当在 java 方法中没有通过 @Param 注解指定参数名时,列表类型默认参数名为 ”list“,数组类型默认参数名为 ”array“,Map 对象没有默认值。
具名参数:java 方法中使用了 @Param 注解指定了参数名称,则 foreach 中的 collection 属性必须为参数名。
insert场景 - VALUES foreach
<insert id = "insert">
INSERT INTO t_test (<include refid="insert_column"/>)
VALUES
<foreach collection="testDatas" item="testData" separator=",">
(#{testData.name},
#{testData.alias})
</foreach>
</insert>select、update场景 - where foreach
<select id = "select">
select <include refid="all_column" />
from t_test
where `test_name` in
<foreach item="oneTest" collection="testNames" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{onetest}
</foreach>
</select>动态where-where标签
mybatis的select语句中,where关键字可以不写死在sql中,如果所有where条件都符合动态场景,where关键字可以直接写成where标签。例如:
<select id="selectStudentsByIf" resultMap="studentMap">
select * from `student`
<where>
<if test="name!=null and name != ''">
`name`like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
<if test="age!=null">
AND `age`=#{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>动态set - set标签
与where同理,update语句的set关键字也可以不写死在sql中,如果所有set值都符合动态场景,set关键字可以直接写成set标签。例如:
<update id="updateStudentBySet" parameterType="com.tick.tack.manager.entity.Student">
update `student`
<set>
<if test="name != null and name !=''">`name`=#{name},</if>
<if test="age!=null">`age`=#{age},</if>
</set>
where `id`=#{id}
</update>分支选择 - choose、when、otherwise
类似java的switch、case、default,语句中的参数可能出现多种情况中的一种,就适合使用分支标签:
<select id="selectStudentByChoose" resultMap="studentMap">
select * from `student`
<where>
<choose>
<when test="name!=null and name != ''">
`name` like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</when>
<when test="age!=null">
AND `age`>=#{age}
</when>
<otherwise>
AND 1=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>灵活条件 - if标签
if语法是test=”条件1 and 条件2”,当test语句中的判断条件为true时,才执行if语句中包裹的语法。例如
<select id="select">
select * from t_test
where student_index > 0
<if test = “age != null and age != ‘’”>
and student_age > #{age}
</if>
</select>set改写版本 - trim标签
trim标签是用来改写set语句的,用法和foreach类似,指定改写的是set,指定语句的拼接符。例如:
<update id="updateStudentByTrimSet" parameterType="com.tick.tack.manager.entity.Student">
update `student`
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null and name !=''">`name`=#{name},</if>
<if test="age!=null">`age`=#{age},</if>
</trim>
where `id`=#{id}
</update>其中suffixOverrides属性就是表名name和age之间用逗号拼接
数据库间的复用 - bind标签
bind标签是应对不同数据库如oracle、mysql等的拼接函数或连接符不同而产生的。
<select id="selectWebsite" resultType="net.biancheng.po.Website">
<bind name="pattern" value="'%'+_parameter+'%'" />
SELECT id,name,url,age,country
FROM website
WHERE name like #{pattern}
</select>mapper编写技巧
字段映射
数据库表字段名称与mapper对应实体类中的属性名称不一样时,没法自动注入数据,解决方案:
起别名,通过
select xx as yy的形式,xx是数据库列名,yy是实体类属性名当sql太多,可以定义引用片段,通过include把查询内容引过去
<sql id="brand_column">
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
</sql>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select <include refid="brand_column" />
from t_brand
</select>定义resultMap:id定义主键映射,result定义其他字段映射
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="com.test.entry.BrandPO">
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"/>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from t_brand
</select>resultMap和resultType的区别:resultType是一种基础类型返回,resultMap是自定义类型一一映射的。
传参查询
对于传参查询,即where语句,可以写where = ${xx},mapper对应的实体类就可以有传参,${}中的内容名与传参名一致
但是使用${}还不如使用#{},因为#{}可以防止sql注入,它的作用是预编译处理,在MyBatis处理#{}时,会将其解释为?处理,这就与JdbcTemplate类似了
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from t_brand
where status = #{status}
and brand_name = #{brandName}
</select>此外,使用<select>标签中的parameterType属性可以设置参数类型
转移字符
在where条件中,<和>会被xml判定为标签的起止符,因此实际mybatis会使用<和>代替<和>,直接替换即可
注意其中的分号;
where status > 1也可以使用cdata区,敲CD创建一个cdata区,里面可以直接写<或>
where status <![CDATA[<]]> 1多参数查询
可以在DAO层接口的接口方法中通过@Param设置多参数,如下:
List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status") int status, @Param("companyName") String companyName,
@Param("brandName") String brandName);指定了status传给status,companyName传给companyName等
也可以把这些参数封装成一个对象或一个map,直接传对象或map进去,但是map的形式并不好
动态条件查询
myBatis支持的动态语句有if、choose、trim(where、set)、foreach四种标签
案例一、if条件查询
允许当用户输入的某个变量(例如companyName)为空时,不执行它(例如companyName)的匹配条件
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from t_brand
where 1 = 1
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="brand_name != null">
and brand_name = #{brandName}
</if>
</select>只要使用多参数查询传递进来对应的status、brandName即可
使用1=1,后面都加and的好处是,第一个变量也可以置空,否则第一个变量写where <if>status = #{status}</if>,如果status为空,会导致sql语句异常
案例二、choose条件选择
类似java中的switch
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from t_brand
where 1 = 1
<choose>
<when test="status != null">
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName != null">
company_name like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName != null and brandName != ''">
brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
</choose>
</select>为了防止一个变量都不传,可以在最后一个<when>后面写一个<otherwise>1=1</otherwise>,作为保底条件
对于动态查询的判断和预编译参考MyBatis源码部分
insert的拓展
Mybatis的insert操作返回void,可以通过catch异常来判断添加是否成功
如果想让insert语句返回插入的主键值,只需要增加属性:
<insert useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">insert语句如果遇到是手动提交的场景,可以使用sqlSession.commit()执行提交
如果想要批插,还可以结合foreach标签:
<insert id="insert">
INSERT INTO `t_test_customer` (
<include refid=”all_column”>
) VALUES
<foreach collection="customers" item="customer" index="index" separator=",">
(
#{customer.name},
#{customer.telephone},
#{customer.address}
)
</foreach>
</insert>update的拓展
update可以主动使用int接收结果,返回修改行数
避免update语句因为传空参报错,可以结合if标签使用:
<update id="update">
update t_brand
set
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != ''">
brand_name = #{brandName}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != ''">
company_name = #{companyName}
</if>
where id = #{id}
</update>或者更保险一点,把set语句也放进if判断中避免任何一个值不传导致空set报错
此外,对表的alter操作也可以使用update标签
<update id="addDatabaseType">
alter table `tttt `
add column `mmm` varchar(16) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL COMMENT "测试字段"
</update>批量update语句存在where in形式的集合判断,也可以结合foreach标签进行模拟:
<update id="updateStudentInfo">
update t_studentInfo set `status`=#{status} where `id` in
<foreach item="item" collection="studentIds" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</update>模拟出来其实就是where id in ("yyty", "xxx", "aaA")这种效果
delete的拓展
delete标签可以做数据删除
// dao.java接口方法
int cleanService(@Param(“aimTime”)Timestamp aimTime);# dao.xml接口实现方法
<delete id="cleanService">
DELETE
FROM test
WHERE `status` = 2
AND `createTime` < #{aimTime}
limit 1000
</delete>

评论区